Difference between revisions of "Refraction"
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[[File:Fitcurve.png|frame|right|Example Curve Fit to multi-layer]] | [[File:Fitcurve.png|frame|right|Example Curve Fit to multi-layer]] | ||
[[File:Twolayer.png|frame|left|Example Two Layer Refraction]] [[File:Multilayer.png|frane|center|Example multi-layer reraction]] | [[File:Twolayer.png|frame|left|Example Two Layer Refraction]] [[File:Multilayer.png|frane|center|Example multi-layer reraction]] | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
==Expert== | ==Expert== | ||
Revision as of 14:31, 1 April 2020
Introduction
Refraction is the word used to describe the phenomenon of a change in direction that an electromagnetic wave travels in.[1] Electromagnetic radiation (which includes light) is observed to change direction when it's velocity changes. How much this velocity differs from the velocity in a vacuum is commonly called the refractive index. The vacuum value is set to 1 for all wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation.
This property of a medium has a few different names.
| NAME |
|---|
| Index of Refraction |
| Refractive Index |
| Optical Density |
| Relative permittivity and permeability |
Beginner
Advanced
It is commonly believed that the absolute value of the refractive index is what causes electromagnetic radiation to bend. This is an incorrect view. The change of direction of electromagnetic radiation occurs when the absolute refractive index along an arbitrary path of travel changes.
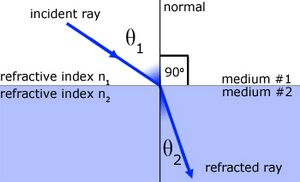
The magnitude of change in the direction of the electromagnetic radiation is related to the magnitude of the difference in refractive indexes. This can be modeled as a discrete boundary (Snell's Law). In this case, the relative refractive index values at the boundary determine the change in direction. The standard usage of this model is when the medium has a well-defined boundary between two isotropic homogenous mediums.
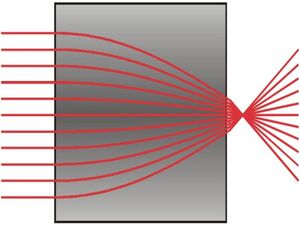
Refraction can also be modeled as a continuum according to Fermat's principle of least time. This method is necessary to model the path of electromagnetic radiation through certain types of mediums. The conditions for usage would be for mediums that have one or more of these properties: ill-defined boundaries, are inhomogeneous, are anisotropic.